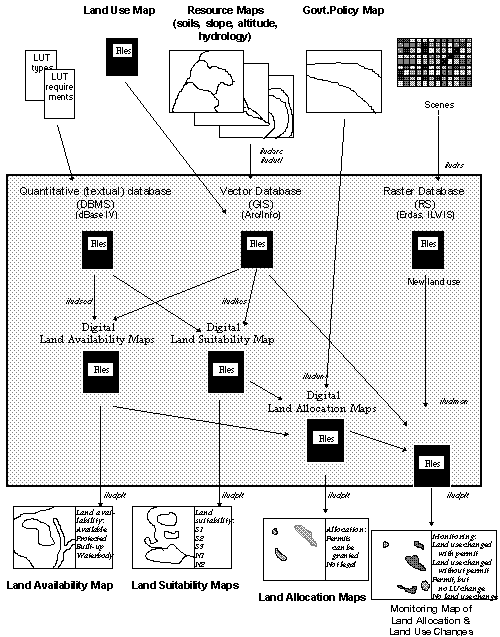
6. Methodology and Techniques: Spatial Land Use Management Planning (Land Allocations)
ILUD Software for Land Allocation
BPN has the task to execute land use planning through the issue of location permits, including their control and monitoring. Particularly, the latter: control and monitoring of permits, was not handled efficiently and consistently in the past. The described GIS system ILUD includes these activities, to support BPN in its task.
Chart of Planning Procedures (of 'Concept' chapter)
6.1 Availability of Land under the Actual Land Use and Legislation
Land can only be allocated to new land use pattern, if the actual land use under the land use legislation permits it. In Indonesia, land can not be allocated to new land uses, where steep slopes or shallow soils can not maintain a sustainable use, where land would be taken out of the main food production cycle (paddy rice land), along rivers in 50 m corridors, in already built-up areas, or in already assigned land. Most of these regulations are defined as presidential degrees.
The processing (overlay of land use, slope, altitude, hydrology, already allocated land) is done with module ILUDSed.
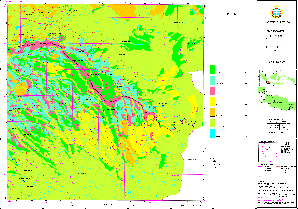
Sample for Land Availability Map: (Cisarua)
(Click map for large size display)

6.2 Land Evaluation
The physical land evaluation basically follows the concept of FAO’s framework for land evaluation, with the definition of land utilization types, land characteristics, land qualities, suitability ratings of S1-N2.
As data sources, resources maps with information about slope, altitude, drainage, erosion status, texture, drainage are linked and matched with the requirements of land use types (land utilization types, here called 'sectors'). At the present 20 of those types are defined with their requirements:
As soon as more data types become available and need arises for more detailed assessment, they will be incorporated.
For user-friendly application, high performance and standardized output, a module to execute land evaluation, i.e. to assess the suitability in terms of suitable and unsuitable classes (S1, S2, S3, N1, N2) for specific land utilization types has been developed (module ILUDKes). It overlays slope, soils, and altitude maps, evaluates the suitability for the selected land use type for each land characteristic, and summarizes based on the limiting factor approach.
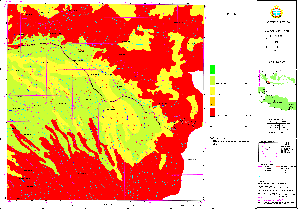
Sample for Land Suitability Map: Tea (Cisarua)
(Click map for large size display)
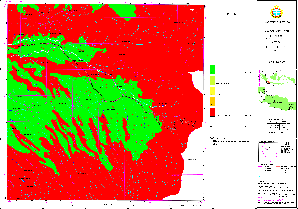
Sample for Land Suitability Map: Urban (Cisarua)
(Click map for large size display)
6.3 Government Policy for Development
These maps are ‘input maps’ to the spatial land use management procedure. They have been defined by planning councils at various levels, not by BPN, partly based on the findings of the previously explained two maps (land availability map and land suitability maps).
Sample for Government Policy Map: (Cisarua)
(Click map for large size display)
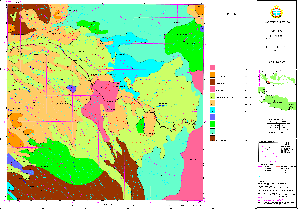
6.4 Land Allocation ('Spatial Land Use Management Plan')
With the two assessments of land availability and land suitability (see Part 6.1 and 6.2) and with the third input of Government policy, where land use should be developed according to the 5-year Development Plans of Indonesia (at national, provincial, or district level), land can be allocated.
The execution of this double overlay is done with module ILUDUnt.
Example: A housing complex can only be permitted, if the suitability is good (not steep slope), the availability is given (not replacing rice land), and where the development policy does not declare other priorities.
Sample for Land Allocation Map: Tea Plantation (Cisarua)
(Click map for large size display)
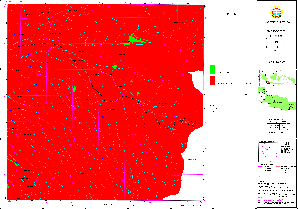
Sample for Land Allocation Map: Urban Extension (Cisarua)
(Click map for large size display)
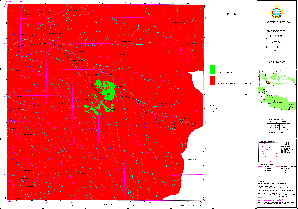
Sample for Land Allocation Map: Afforestation (Cisarua)
(Click map for large size display)
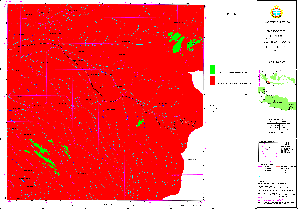
Monitoring is understood at two stages: At the first step, it is the detection of land use changes, i.e. taking two land use maps of different years and compare them. (Overlay of two maps to define units, which are not equal).
At the next level - and more important in terms of land use control - is the integration of issued location permits to the land use change detection. There are following units resulting from such an overlay:
Tab.6: ILUD Cycle for Spatial Land Use Management Planning
|
Step |
Task |
Com-ponent |
Module |
Result |
Time (1)
|
|
1 |
Assess current land use |
GIS |
described above |
Digital land use map |
(4-15 days) (2) |
|
2 |
Check/Convert additional input maps |
GIS |
ILUDUtl |
Digital maps of: slope, hydrology, soils, altitude, Govt.policy |
20 min - 2 days |
|
3 |
Assess land availability |
GIS |
ILUDSed |
Land availability map |
20-30 min |
|
4 |
Assess land suitability |
GIS |
ILUDKes |
Land suitability maps (for particular land uses) |
10-20 min |
|
5 |
Assess land for allocation permits ('spatial land use management plan') |
GIS |
ILUDUnt |
Land allocation maps (for particular land uses) |
10-20 min |
|
6 |
Monitor changes |
GIS |
ILUDMon |
Monitoring map |
10-20 min |
|
7 |
Plot any of those maps |
GIS |
ILUDPlt |
Hardcopy map |
20-40 min |
(1) Per map sheet
(2) Data collected/processed per 'study area', time given on pro-rata basis
Sample for Land Use Map: Recent (Pesalakah/Bali)
(Click map for large size display)
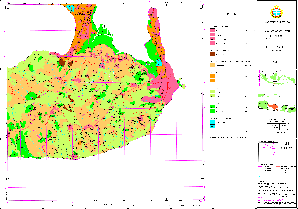
Sample for Land Use Map: Previous (Pesalakah/Bali)
(Click map for large size display)
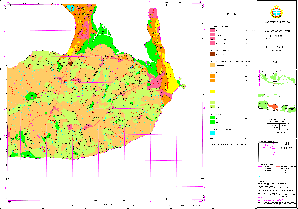
Sample for Monitoring (Land Use Change Detection): Recent (Pesalakah/Bali)
(Click map for large size display)
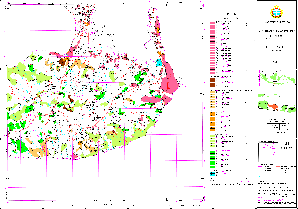
Sample for Monitoring (including location permits): Recent (Pesalakah/Bali)
(Click map for large size display)
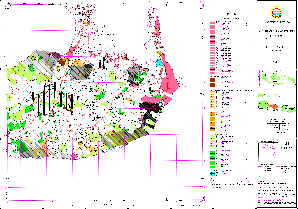
Tab.7: Individual Processes of Spatial Land Use Management Planning
|
|
Step |
Process |
Processes |
Commands |
|
1 |
Assess land use |
Described in Part 5 |
|
|
|
2 |
Check/Convert additional input maps |
Check manually Make user ids unique Standardize file structure Convert with reference files ILUDUtl...dbf |
AI: tables.items AI: tables.calculat - idedit - build AI: additem - dropitem AI: joinitem |
|
|
3 |
Assess land availability |
Check all file structures Convert all to UTM Create buffers along rivers Overlay rivers with slope Overlay result with location permits Overlay result with land use Eliminate small units Adjust file structure Convert to lat/long Assignment of areas |
AI: project cover AI: buffer AI: identity AI: identity AI: intersec AI: eliminat AI: additem - dropitem AI: project cover dB: replace ... for ... AI: dissolve |
|
|
4 |
Assess land suitability |
Selection of land use type Check all file structures Convert all to UTM Overlay soils with slope Overlay result with altitude Overlay result with land use Eliminate small units Read requirements of land use type Adjust file structure Convert to lat/long Assignment of areas |
AI: project cover AI: intersec AI: intersec AI: intersec AI: eliminat AI: joinitem - modify AI: additem - dropitem AI: project cover dB: replace ... for ... AI: dissolve |
|
|
5 |
Assess land for allocation permits |
Selection of land use type Check all file structures Convert all to UTM Overlay suitability with availability Overlay result with Govt.policy Eliminate small units Adjust file structure Convert to lat/long Assignment of areas |
AI: project cover AI: identity AI: identity AI: eliminat AI: additem - dropitem AI: project cover dB: replace ... for ... AI: dissolve |
|
|
6 |
Monitor changes |
Check file structures Convert to UTM Overlay old with new land use map Convert to lat/long Adjust file structure Assignment of classes Eliminate small units |
AI: project cover AI: intersec AI: project cover AI: dropitem dB: replace AI: eliminat |
|
|
7 |
Plot of any of those maps
|
(see above) Monitor map with option to overlay 'Location permits' as shading |
|
Fig.7: 'Spatial Land Use Management' Methodology (ILUD Cycle)
for Allocation of Location Permits and Its Monitoring