5. Methodology and Techniques: Land Use Mapping
ILUD Software for Mapping
The methodology to execute above mentioned concepts and to achieve the requested tasks can be split into two major parts:
5.1 Methodology for land use mapping
5.1a Land use mapping from aerial photographs
If aerial photos are the primary data source, aerial photo interpretation will be undertaken with delineation of homogenous ‘API units’ with stereoscopes. This is followed by fieldwork, where for each defined mapping unit (not for each polygon) 1-10 samples are taken and their land use is described. Such a description both in terms of land use indicators (e.g., distance of houses, height of trees, etc. for the functionality: 'land use', not only 'land cover') as well as in terms of predefined land use classes is important because these data will be used for medium and large scale survey. Additionally, land use indicators (descriptions) can be used to check vs. the classification.
The delineation of API will be digitized (using software module ILUDArc). Photo codes, which do not directly indicate the land use, are entered as polygon identifiers. This is called ‘labeling’ and is handled by module ILUDLab.
Field data are entered in the DBMS with module ILUDEntr, processed with ILUDProc to assess the relationship between the photo interpretation codes and the actual land use (from the field descriptions). The result indicates, which land use class(es) occur(s) in each photo unit. This is then linked to the GIS data (with ILUDLab).
The linked maps contain information about primary and secondary land use with their ratio, their numerical code, and their character code (abbreviation). It includes additional parameters such as the number of the province, the year of the survey, a quality control figure, and the software version (see Annex for a sample of the attribute data of the land use maps).
All this information is automatically added during the linkage procedure with module ILUDLab. Topology is complete. Due to the size of Indonesia stretching over 9 UTM zones (90º - 144º E), and to keep all georeferences unique, data are always stored in geographical units (latitude/longitude).
The map can then be plotted with module ILUDPlt, which includes a formal data integrity check (data completeness), for complete topology, for correct georeference etc. This is part of the quality assurance of the digital data. The plot can be done on a plotter or printer in any size. Alternatively, final maps can be transferred to other graphic formats (see also Part 7.2 and Annex).
The plotted hardcopy maps follows a standard map layout based on the national grid system. Optionally, maps can be plotted based on administrative boundaries, e.g. for a District or a Subdistrict (with preparation through ILUDAdm, which ‘clips’ and aggregates map sheets).
Care is taken for these cases if two substantially different land uses occur in one mapping unit, i.e. sparsely settled villages between fruit trees (in Indonesia called 'mixed gardens', or fish ponds in a mixed pattern with paddy rice fields). These cases can not be differentiated by photo interpretation, but they are often obvious in the field. These are 'complex units' and are identified both in the databank (with their ratio) and on plotted land use maps.
Tab.1: ILUD Cycle for Land Use Mapping from Aerial Photographs
|
Step |
Process |
Com-ponent |
Module |
Result |
Time (1)
|
|
1 |
Aerial photo interpretation |
- |
(manually) |
Manuscript map ('API map') |
1-4 days |
|
2 |
Field work |
- |
(manually) |
Field data sheets |
1-4 days (2) |
|
3 |
Entry of field data |
DBMS |
ILUDEntr |
Data file with land use descriptions |
½-2 days (2) |
|
4 |
Processing of field data |
DBMS |
ILUDProc |
Data file with info about photo codes |
10-30 min |
|
5 |
Digitization of arcs |
GIS |
ILUDArc |
Raw digitized map ('Z coverage') |
1-3 days |
|
6 |
Labeling of polygons |
GIS |
ILUDLab |
Map coverage with labels and topology |
½-1 day |
|
7 |
Link DBMS - GIS |
GIS |
ILUDLab |
Digital land use map |
5-20 min |
|
8 |
Conversion to lat/long |
GIS |
ILUDCon |
-"- |
3-5 min |
|
9 |
Clipping |
GIS |
ILUDUtl |
-"- |
10 min |
|
10 |
Plotting |
GIS |
ILUDPlt |
Hardcopy map |
20-40 min |
|
11 |
Backup |
GIS |
ILUDUtl |
Backup copy |
1-3 min |
(1) Per map sheet
(2) Data collected/processed per ‘study area’, time given on pro-rata basis
Various alternative approaches have been practiced and are installed in the system, such as digitization from aerial photographs, digitization of observation points from the tablet, transfer of observation points from DBMS to GIS and v.v., different generalization levels, selection between two land use classification systems, conversion from digitizer units to lat/long or UTM, manual editing of labels at map plot, etc.
Fig.5: Land Use Mapping Methodology (ILUD Cycle)
for Assessment of Current Land Use

Tab.2: Individual Processes of Land Use Mapping from Aerial Photographs
|
|
Step |
Process |
Processes |
Commands |
|
|
1 |
API |
Delineation of homogenous units Assignment of 'API codes' (not land use classes) (Semi)controlled mosaic Transfer to base map |
- |
|
|
2 |
Field work |
Field work design (stratified, random, clustered sampling method) Field descriptions Field correlation matrix |
- |
|
|
3 |
Entry of field data |
Define dbf file (if new survey year) Add new record for each observ. site Enter data for each site (controlled, checked and coded) |
dB/Cl5: copy structure dB/Cl5: append blank dB/Cl5: replace |
|
|
4 |
Processing of field data |
Searching for 'API codes' For each 'API code': Search for all observations with the 'API code' Assignment of dominant land use class(es) per 'API code' Transfer to 'polygon attribute' dbf file |
dB/Cl5: asort dB/Cl5: array calculations dB/Cl5: copy structure - append blank - replace |
|
|
5 |
Digitization of arcs |
Create coverage Avoid double user ids Digitize arcs Delete /Split arcs Move nods Clean arcs ('overshoots') and Checks |
AI: create AI: calculat $id AE: ef arcs - add AE:ef arcs - delete - split AE: ef node -move clean |
|
|
6 |
Labeling of polygons |
Build topology Create one label per polygon Assign label |
AI: build AI: createla - calculat - idedit - build AE: ef labels - moveitem |
|
|
7 |
Link DBMS - GIS |
Check/clean file structure Merging result from DBMS (PA dbf file) to coverage for extended attr.table |
AI: build - dropitem - tables.list AI: joinitem - additem |
|
|
8 |
Conversion to lat/long |
Check for georeference (UTM or lat/long or dig. units) Option of direct or tic-based conversion Convert Re-build topology |
AI: tables.list AI: project cover AI: build |
|
|
9 |
Clipping |
Mathematical calculation of map frame acc. national grid Convert coverage+map frame to UTM Standardize fuzzy tolerance 1.clipping, 10% outside frame 2.clipping, precise Rebuilding topology |
AI: generate.lines AI: project cover delete TOL. AI: clip AI: clip AI: build |
|
|
10 |
Plotting |
Many checks for topology, labeling etc. Convert to UTM Creation of plot file with all features Plot |
AI: tables.list AI: project cover AP: displ 1039 hpgl2 - x.hp2 |
|
|
11 |
Backup |
Compress all GIS coverages and associated DBMS data per sheet |
pkzip |
Various quality control checks ('formal data integrity checks') are integrated in the software modules, such as:
A number of utility sets are available, e.g. for:
If the software modules are being applied, there is no concern for deviation from the standard and the application of the data dictionaries: Automatically, the programs (ILUD modules) apply the standard codes and the data become formally integer and clean.
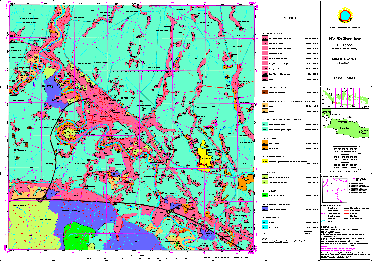
Sample for Land Use Map: West-Jawa (Karawang)
(Click map for large size display)
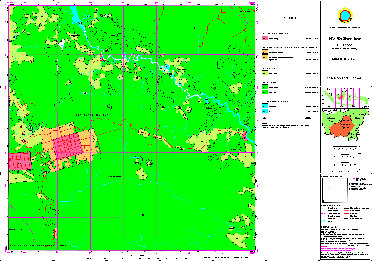
Sample for Land Use Map: Kalimantan (1614-522)
(Click map for large size display)
5.1b Land use mapping from satellite images
If satellite images are available, image processing of the scenes will be done in Erdas (7.5 or Imagine) with ILUD image processing menu and spectrally classified.
The image processing includes data import, enhancement, geometric correction, unsupervised classification with 27 classes, check of GIS file signature with image LAN file, optionally merging of signatures of obvious identical land use classes, assignment of new colors, and finally filtering of 3x3 for TM images. |
The approach of an unsupervised classification was chosen because of the inexperience of the staff, the complex land use patterns, which can not be differentiated with spectral classification signatures, and the stress of large scale inventory and mapping for land use planning and land allocation permits. Collection of field data is not a major problem at the institution and results in more reliable data about land use definitions.
After conversion to vector format in the GIS (with module ILUDR2v), this ‘spectral classification map’ is taken to the field and serves as a basis for the field data collection. Further processing is identical to above described procedure from the aerial photo interpretation, including the ‘labeling’ for land use classification, field work, and field data entry.
Tab.3: ILUD Cycle for Land Use Mapping from Satellite Image
|
Step |
Task |
Com-ponent |
Module |
Result |
Time (1)
|
|
1 |
Image processing |
IP |
ILUD image processing menu system |
Classified image file |
½ - 2 days
|
|
2 |
Transfer to GIS (vector) |
GIS |
ILUDR2v |
Spectral classifi- cation coverage |
½ - 4 hrs |
|
3 |
Plotting of remote sensing result |
GIS |
ILUDPlt |
Hardcopy map of spectral image |
20-40 min |
|
4 |
Field work |
- |
(manually) |
Field data sheets |
1-4 days (2) |
|
5 |
Entry of field data |
DBMS |
ILUDEntr |
Data file with all land use descriptions |
½-2 days (2) |
|
6 |
Processing of field data |
DBMS |
ILUDProc |
Data file with info about photo codes |
10-30 min |
|
7 |
Labeling of polygons (per spectral class) |
GIS |
ILUDLab |
Map coverage with labels and topology |
15 min
|
|
8 |
Link DBMS - GIS |
GIS |
ILUDLab |
Digital land use map |
5-20 min |
|
9 |
Plotting |
GIS |
ILUDPlt |
Hardcopy map |
20-40 min |
|
10 |
Backup |
GIS |
ILUDUtl |
Backup copy |
1-3 min |
(1) Per map sheet
(2) Data collected/processed per ‘study area’, time given on pro-rata basis
Tab.4: Individual Processes of Land Use Mapping from Satellite Images
|
|
Step |
Process |
Processes |
Commands |
|
|
1 |
Image processing |
Data input Enhancement Geometric correction Unsupervised classification Check of GIS file signature Filtering |
E: bstat E: gcp - coordn - nrectify E: isodata E: colormod E: scan - majority filter 3x3 |
|
|
2 |
Transfer to GIS (vector) |
Convert to vector format Clip in two steps (+10%, precise) Standardize fuzzy tolerance Standardize file structure Read color assignments Eliminate small units Unique user ids Merge lines Smoothen lines
Convert to lat/long |
AI: gridpoly AI: clip - build delete tol. AI: additem Pascal program AI: eliminat AI: tables.calculat - idedit - build AI: renode AE: unsplit AI: generaliz AE: grain (3 times) AI: project cover |
|
|
3 |
Plotting of remote sensing result |
Convert to UTM Creation of plot file with all features Plot |
AI: project cover AP: displ 1039 hpgl2 - x.hp2 |
|
|
4 |
Field work |
(same as API) |
|
|
|
5 |
Entry of field data |
(same as API) |
|
|
|
6 |
Processing of field data |
(same as API) |
|
|
|
7 |
Labeling of polygons (per spectral class) |
Build topology Assign labels |
AI: build AE: ef lables - sel for ... moveitem |
|
|
8 |
Link DBMS - GIS |
(same as API) |
|
|
|
9 |
Plotting |
(same as API) |
|
|
|
10 |
Backup |
(same as API) |
|
Sample for Spectral Classification Map: (2305-423)
(Click map for large size display)